According to the Prohibited List, certain asthma medications are prohibited. At the same time, there are many permitted medications available, which can be used for asthma. For permitted therapies, no therapeutic use exemption (TUE) is required.
Two of the most common groups of substances used in asthma therapy are on the current Prohibited List: beta-2 agonists and glucocorticoids. However, for both groups of substances there are clearly defined exceptions that are listed in the Prohibited List.
Beta-2 agonists
All beta-2 agonists are prohibited, except for the inhalation of:
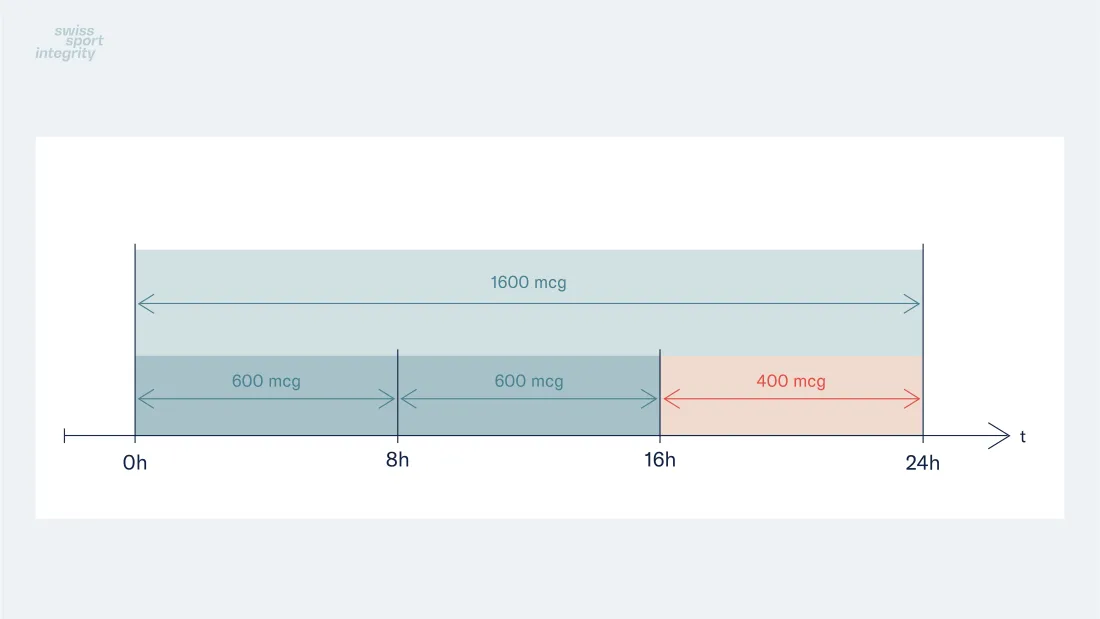
- Salbutamol: maximum 1600 micrograms over 24 hours in divided doses not to exceed 600 micrograms over 8 hours starting from any dose;
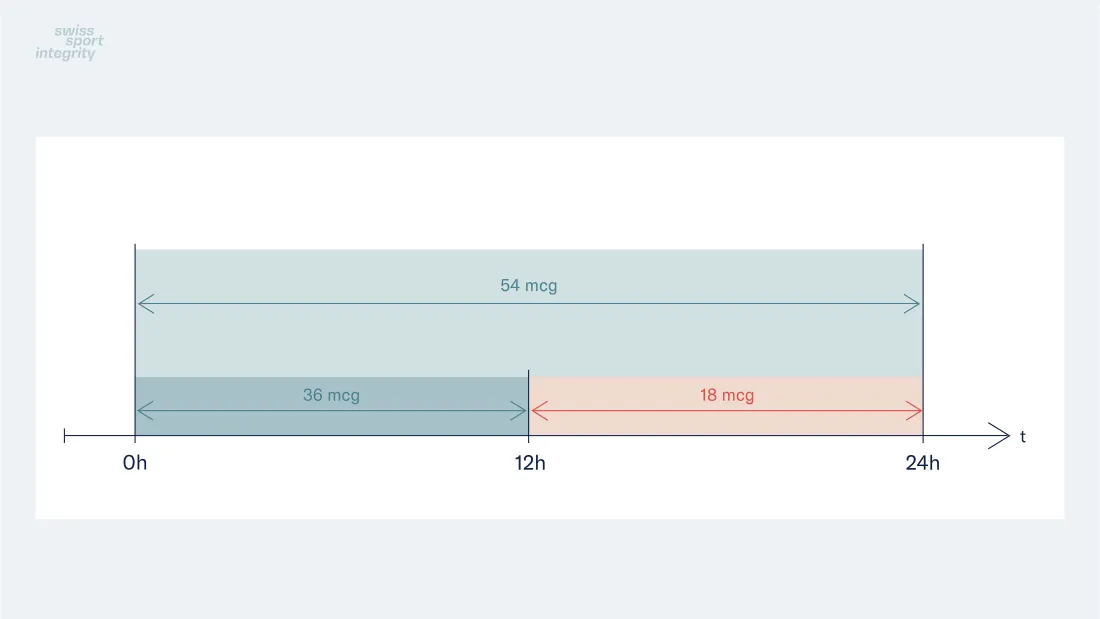
- Formoterol: maximum delivered dose of 54 micrograms over 24 hours in divided doses not to exceed 36 micrograms over 12 hours starting from any dose;
- Salmeterol: maximum 200 micrograms over 24 hours;
Starting from 1.1.2026: maximum 200 micrograms over 24 hours in divided doses not to exceed 100 micrograms over 8 hours starting from any dose; - Vilanterol: maximum 25 micrograms over 24 hours.
These thresholds do not apply if in addition to the beta-2 agonists prohibited diuretic or masking agents are used. In this case, a TUE is required for both therapies.
Glucocorticoids
All glucocorticoids are prohibited in competition when administered by any injectable, or rectal route. Other routes of administration, such as inhalation, are thereby permitted.
Permitted Therapies
In most cases, these rules allow for basic and need-based therapy with permitted medication. For permitted asthma therapies, as for all other permitted therapies, no TUE is required according to the current anti-doping rules.
However, if a TUE application for permitted therapies is sent to Swiss Sport Integrity, it will be returned with reference to this website and without evaluation. If you are unsure whether a therapy is permitted or prohibited, please contact us before submitting a TUE application.
Applications for therapies with prohibited inhalative asthma medication can only be approved in well-founded exceptional cases, since there are permitted therapies according to the Prohibited List. If a prohibited therapy is suggested by the treating physician, clarify whether a permitted alternative can be prescribed.
Prohibited Therapies
If there is a necessity for a prohibited therapy, in addition to the usual medical documentation and diagnosis, a comprehensive medical justification why no permitted therapy alternative can be used is required (e.g. documented therapy failure of permitted medication, including pulmonary function test). If such a justification is missing, inadequate according to the applicable regulations or not comprehensible to the TUE committee, no TUE will be granted.
For medical emergencies and the use of prohibited glucocorticoids, please refer to the relevant information.
Example Threshold Dose of Salbutamol
Example Threshold Dose of Formoterol
Example Interpretation of Search Results on Global DRO

Warning: Nebulization is Prohibited
The use of salbutamol by nebulization is prohibited according to the Prohibited List, as the doses administered exceed the applicable threshold. Therefore, a TUE is required. However, the approval of a TUE for this therapy is only conceivable in very rare cases, for example for the treatment of a severe asthma attack in an emergency ward.